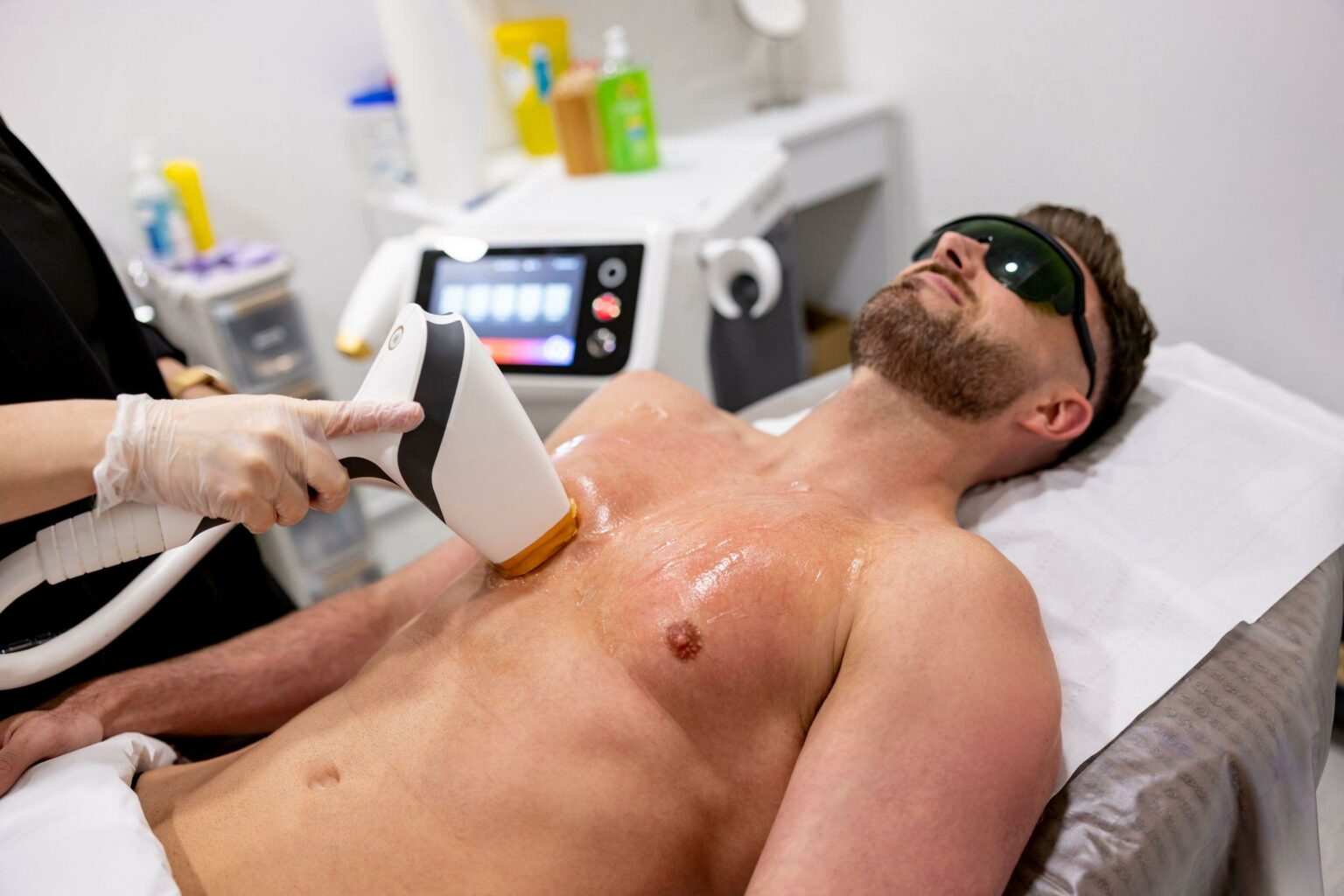
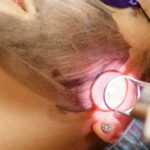
In the realm of modern cosmetic enhancements, laser technology has commanded a focal point, offering an array of transformative possibilities. One of the most sought-after treatments is laser hair removal, celebrated for its ability to deliver smooth, hair-free skin with minimal discomfort. However, beneath the allure of its convenience lies a critical question: what impact does this powerful technology have on the melanocytic nevi, commonly known as moles, scattered across our canvas of skin? This article delves into a meticulous study that seeks to illuminate this very query, exploring the delicate interplay between laser light and the pigmented entities upon our bodies. Join us as we unravel the findings, implications, and potential pathways for future dermatological practice in the intriguing intersection of laser hair removal and melanocytic nevi.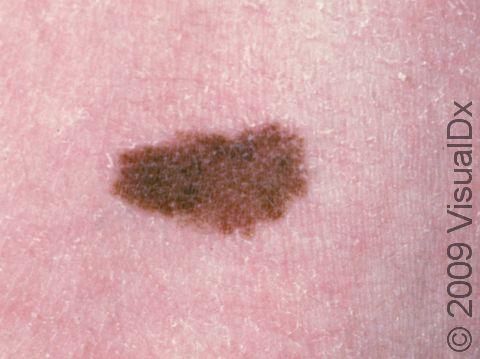
Understanding Melanocytic Nevi and Laser Hair Removal
The intersection of **laser hair removal** technology and skin health, particularly regarding melanocytic nevi, is a topic of heightened interest and diligent study. These pigmented lesions, commonly known as moles, can often be present in areas where laser hair removal treatments are sought. Understanding their interaction with laser technology is vital for ensuring both aesthetic and medical outcomes are optimized.
Laser hair removal works by targeting melanin, the pigment responsible for hair color, which absorbs the laser energy and converts it into heat. This process destroys the hair follicle but also raises questions about its impact on melanocytic nevi. **Potential impacts** include:
- Changes in pigmentation
- Altered morphology
- Possible irritation
Ensuring that these moles are properly monitored before, during, and after laser treatments mitigates any undue risk.
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Hyperpigmentation | Darkening of the nevi after treatment |
| Hypopigmentation | Lightening of the nevi post-procedure |
| Size Changes | Potential increase or decrease in mole size |
For anyone considering laser hair removal who also has melanocytic nevi, a pre-treatment consultation with a dermatologist is prudent. It’s crucial to distinguish between common moles and suspicious lesions that might require further evaluation or even biopsy. **Dermatologists** generally recommend:
- Mapping your moles
- Using physical barriers to protect nevi during laser exposure
- Regular follow-ups to observe any changes
This proactive approach ensures that any potential risk is minimized, balancing cosmetic desires with health considerations.

Delving into the Data: The Studys Methodology and Findings
Our study meticulously analyzed the impact of laser hair removal on melanocytic nevi by employing a robust methodology. This research involved a cohort of participants, each with multiple melanocytic nevi, who underwent a series of laser hair removal treatments. The study spanned over six months, ensuring a comprehensive observation period. To maintain high accuracy, we used advanced imaging technology and dermatoscopic evaluations before and after each session.
**Key aspects of our methodology included:**
- Participant Selection: Individuals with stable, benign melanocytic nevi
- Evaluation Tools: Dermatoscopes and high-resolution imaging
- Control Measures: Consistent laser settings and qualified practitioners
- Assessment Frequency: Pre-treatment and post-treatment evaluations at regular intervals
The results were fascinating and provided significant insights. Upon analyzing the data, we observed that the melanocytic nevi displayed notable changes in specific parameters. These included alterations in pigmentation, size, and symmetry. Interestingly, most nevi exhibited a **reduction in pigmentation** and size, which suggests potential benefits beyond hair removal.
| Parameter | Before Treatment | After Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Average Pigmentation | High | Reduced |
| Average Size | Significant | Reduced |
| Symmetry | Stable | Maintained |
While the findings appeared promising, the study also emphasized the importance of ongoing monitoring and cautious approach. Changes in pigmentation and size may hold potential risks if not consistently evaluated. Hence, our study recommends regular follow-ups and dermatoscopic assessments for individuals undergoing laser hair removal on areas with melanocytic nevi. This ensures early detection of any atypical developments and reinforces the importance of personalized patient care.
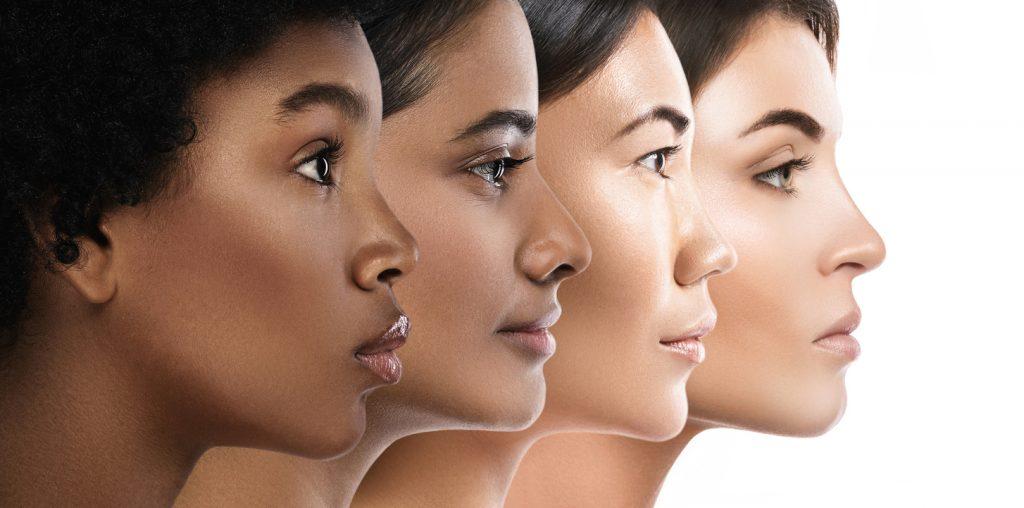

Navigating Risks: Potential Impacts on Different Skin Types
Understanding how laser hair removal might affect melanocytic nevi across different skin types is pivotal for both practitioners and patients. Skin types, typically categorized using the Fitzpatrick scale, range from Type I (very fair) to Type VI (very dark). Each type reacts differently to various cosmetic and medical treatments, including laser hair removal. For instance, individuals with lighter skin types (I-III) generally face fewer pigmentation changes but might be at varied risks when addressing areas with nevi.
On the other hand, **darker skin types (IV-VI)** are more prone to hyperpigmentation and other complications due to the higher melanin content. Melanin absorption can sometimes lead to unpredictable results, elevating the risk for changes in nevi during laser treatments. To mitigate these risks, professionals often suggest patch testing or the use of laser systems with longer wavelengths, which are less absorbed by melanin and thus gentler on darker skin.
- **Type I-III (Lighter Skin)**: Lower risk for pigmentation changes, careful monitoring recommended.
- **Type IV-VI (Darker Skin)**: Higher melanin absorption risks, suggesting longer wavelength systems.
Moreover, it’s crucial to understand the **protocols for pre- and post-treatment care**. Patients with varying skin types should adhere to tailored advice to minimize adverse reactions. For example, individuals with Type I-II skin may primarily focus on sun protection, while those with Type V-VI might need additional interventions like corticosteroid creams to prevent hyperpigmentation. Here’s a quick look at suggested aftercare:
| Skin Type | Aftercare Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Type I-II | SPF 50+, avoid sun exposure |
| Type III-IV | Moisturize, mild steroid creams |
| Type V-VI | Hydrocortisone, monitor pigmentation |
**Collaboration between dermatologists and laser specialists** is vital to navigate these variations effectively. Leveraging this teamwork ensures that the chosen laser technology and settings accurately align with the patient’s skin type, minimizing risks while enhancing the treatment’s overall efficacy. By thoughtfully addressing these nuances, practitioners can better safeguard skin health and successfully manage the impacts on melanocytic nevi during laser hair removal procedures.

Expert Recommendations: Best Practices for Safe Treatments
Ensuring safe treatment practices during laser hair removal is essential, particularly when clients have melanocytic nevi, commonly known as moles. These hyperpigmented areas of skin can react differently to laser exposure, necessitating tailored approaches for effective and safe hair removal sessions.
A crucial aspect of best practices involves a pre-treatment evaluation by a dermatologist or licensed practitioner. This step typically includes:
- Detailed skin assessments
- Documentation of the size, shape, and color of nevi
- Use of imaging tools for accurate monitoring over time
By establishing a clear baseline, any changes induced by the laser treatment can be easily tracked, ensuring no adverse effects go unnoticed.
The selection of appropriate laser wavelengths and energy settings can significantly reduce risks. Dermatologists recommend the following guidelines:
| Laser Type | Recommended Use |
|---|---|
| Alexandrite Laser | Suitable for lighter skin types |
| Diode Laser | Effective for various skin types including darker tones |
| Nd:YAG Laser | Preferable for very dark skin and large areas |
This table provides a quick reference for practitioners, ensuring they select the most suitable laser type for each client’s unique skin composition and nevus characteristics.
Aftercare routines are equally pivotal to maintain skin integrity post-treatment. Recommended aftercare includes:
- Application of soothing topical agents such as aloe vera
- Avoidance of direct sunlight and use of SPF 50+ sunscreen
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor skin healing
Consistent adherence to these practices not only promotes healing but also minimizes potential complications, ensuring optimal results for clients.
Looking Forward: Innovative Approaches and Future Research Directions
As we venture into the evolving landscape of laser hair removal (LHR) and its effects on melanocytic nevi, several innovative approaches are beginning to capture the attention of researchers and clinicians alike. One promising avenue is the utilization of **advanced imaging techniques**, such as high-resolution dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy, to meticulously monitor the morphological changes in nevi post-LHR treatments. These imaging modalities can afford unparalleled insight into the subtle alterations that could signify either benign or malignant transformations, thus enhancing early detection and intervention strategies.
- Dermoscopy: Offers detailed visualization of nevus structure.
- Reflectance Confocal Microscopy: Provides in vivo microscopic examination of nevi.
Another groundbreaking approach is the integration of **artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)** models into dermatological research. These technologies can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predictive markers within melanocytic lesions. By training AI algorithms on images and histopathological data, researchers aim to develop predictive tools that can preemptively flag nevi that are likely to undergo malignant transformation following LHR.
| Technology | Function |
|---|---|
| AI Algorithms | Pattern recognition in nevi |
| Machine Learning | Predictive marker identification |
Exploring **combination therapies** also holds significant potential for future research. The simultaneous or sequential use of LHR with topical agents or systemic medications that can modulate nevus behavior might offer a two-pronged approach to managing nevi effectively. This could minimize the risk of adverse transformations and optimize aesthetic outcomes, thus providing a more comprehensive care strategy.
- Topical Agents: Enhancing skin barrier and pigment control.
- Systemic Medications: Regulating nevus activity internally.
there is considerable interest in the **genomic profiling of nevi** post-laser treatment. By analyzing gene expression and mutational profiles, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of the molecular pathways that drive nevus response or resistance to LHR. This genomic data could pave the way for tailored treatments and personalized patient management plans, ultimately leading to safer and more effective LHR procedures.
Q&A
Q&A: Laser Hair Removal’s Impact on Melanocytic Nevi: A Study
Q: Can you give us a brief overview of the study covered in the article?
A: Absolutely! The study focuses on examining whether laser hair removal procedures affect melanocytic nevi, commonly known as moles. Researchers aimed to determine if lasers, which are effective for removing unwanted hair, might induce changes in the appearance or cellular structure of these typically benign skin anomalies.
Q: Why was this study deemed necessary?
A: As laser hair removal has gained immense popularity, concerns have risen regarding its safety, particularly in relation to melanocytic nevi. Dermatologists and patients alike wanted clarity on whether the laser treatments could potentially transform benign moles into malignant ones or cause other significant dermatological changes.
Q: What methods did the researchers employ in their investigation?
A: The researchers observed a cohort of participants undergoing laser hair removal treatments. They meticulously documented the initial state of various melanocytic nevi through high-resolution imaging. Subsequent check-ups were conducted at regular intervals post-treatment to monitor any morphological changes in the moles.
Q: What were the key findings of the study?
A: Interestingly, the study revealed that laser hair removal did not induce significant changes in most melanocytic nevi. The majority of moles remained unchanged in size, shape, and color. Only a small fraction exhibited minor, temporary alterations, which subsequently reverted to their original state.
Q: How did the study address concerns regarding the potential risk of malignancy?
A: The research team took a multi-faceted approach by incorporating histopathological analyses. Samples from a subset of nevi were biopsied and inspected for any signs of atypical cells or malignant transformation before and after the laser treatments. The results showed no evidence of induced malignancy or pathological abnormalities.
Q: Were there any limitations identified in the study?
A: Yes, the researchers acknowledged several limitations. One key limitation was the relatively small sample size. They also noted the short follow-up period, suggesting that longer-term studies are essential to corroborate these findings. Additionally, there was a need for more diverse participant demographics to ensure broad applicability of the results.
Q: What implications do these findings hold for the general public and dermatology professionals?
A: The study brings a sigh of relief for both patients considering laser hair removal and dermatology professionals who recommend it. It supports the notion that laser hair removal is generally safe concerning melanocytic nevi. However, it also underscores the importance of individualized assessments and encourages ongoing vigilance and regular skin check-ups.
Q: What future research directions did the authors propose?
A: The authors suggest extended research with larger, more diverse populations and longer follow-up durations. They also advocate for exploring the effects of different types of laser technologies on melanocytic nevi to ensure comprehensive safety profiles across various devices.
Q: what should readers take away from this study?
A: Readers should take away an informed confidence in the relative safety of laser hair removal concerning melanocytic nevi. While the findings are reassuring, it’s still prudent to consult with healthcare professionals, especially when dealing with pre-existing skin conditions. Continuing research and vigilance will always be pivotal in safeguarding skin health.
Closing Remarks
As the laser light fades and our understanding deepens, it’s clear that the relationship between laser hair removal and melanocytic nevi requires thoughtful consideration. The flicker of potential risks calls on both clinicians and patients to navigate this domain with a blend of scientific rigor and caution. While the beam of innovation continues to shape convenience and beauty, let us remain vigilant, ensuring that our quest for the flawless aligns harmoniously with the safeguarding of our health. In a world where knowledge beams ever brighter, may our decisions always be illuminated by wisdom and care.