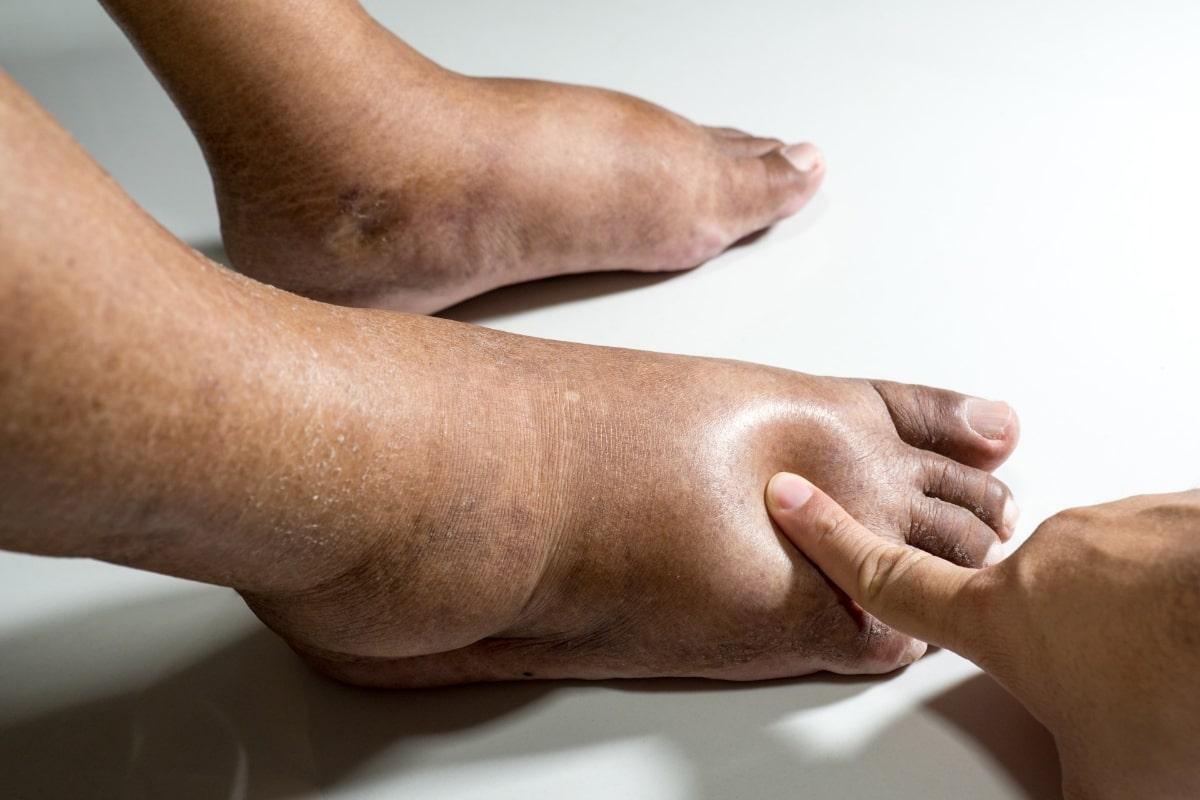
Swollen limbs and puffiness that alter the contour of one’s body can become unwelcome companions in the journey through cancer treatment. This distressing condition, known as edema, often feels like an uninvited guest, adding layers of discomfort to an already challenging path. Navigating the multifaceted world of cancer care can be overwhelming, yet comprehending and managing edema can offer a semblance of control and relief amid the tumult. In this article, we delve into the nuanced interplay between cancer treatment and edema, exploring strategies to manage this condition thoughtfully and effectively, ensuring that the focus remains on healing and resilience. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, join us as we unravel the complexities of managing edema with the care and compassion it necessitates.
Understanding Edema: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Edema, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in body tissues, can stem from a variety of causes. In the context of cancer treatment, several factors related to both the disease and its management can trigger or exacerbate edema. **Chemotherapies**, **radiation treatments**, and even some types of targeted therapies often play a role in fluid retention. Additionally, certain cancers themselves, particularly those affecting the lymphatic system or kidneys, directly contribute to the development of edema. Understanding these causes helps in tailoring effective management strategies.
Identifying the symptoms of edema is critical for timely intervention. Signs often include **swelling** in specific areas such as the ankles, feet, and hands, alongside more generalized symptoms like **tight or shiny skin** and a **feeling of heaviness** in the affected areas. Patients might also experience decreased **flexibility** and **difficulty moving joints**. Early detection of these symptoms can facilitate quicker medical response, ideally mitigating complications before they worsen.
**Recognizing Symptoms:**
- Visible swelling, especially in extremities
- Skin that appears tight or shiny
- Heaviness or difficulty moving affected areas
- Pitting edema (indentation remains when pressed)
Diagnosing the underlying causes of edema involves a combination of physical examinations and diagnostic tests. Physicians often begin with a **comprehensive medical history** and **physical exam** to assess the extent and impact of the swelling. Diagnostic tools such as **blood tests**, **urine analysis**, and imaging tests like **ultrasounds or MRIs** may also be employed. These tests help pinpoint the exact cause, whether it’s related to cancer treatment, organ dysfunction, or another underlying health issue. Early and precise diagnosis is key to developing a targeted and effective treatment plan.

The Connection Between Cancer Treatments and Edema
Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery, are often lifesaving but they come with a myriad of side effects, one of which can be edema. Edema, or swelling, occurs when an excess of fluid accumulates in the body’s tissues. This can be particularly troubling for patients already dealing with the immense challenges of cancer. Understanding the connection and learning how to manage edema can make a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life.
**Chemotherapy** can trigger edema by causing fluid retention as a side effect of certain medications. This fluid buildup can lead to swelling in various parts of the body, such as the hands, feet, or even the face. Patients undergoing chemotherapy should stay informed about their specific medications and discuss potential side effects with their healthcare providers. Implementing lifestyle changes such as reducing salt intake, staying active, and wearing compression garments can help mitigate these effects.
**Radiation therapy** targets cancer cells but can inadvertently harm nearby healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and fluid accumulation. This is particularly common in treatments for cancers of the lymphatic system because the lymph nodes, crucial for fluid regulation, may be compromised. Patients receiving radiation therapy may benefit from regular lymphatic drainage massages and maintaining elevated positions of swollen limbs to reduce discomfort.
| **Type of Treatment** | **Possible Impact** |
|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Fluid retention, Hand/foot swelling |
| Radiation Therapy | Tissue inflammation, Lymphatic disruption |
| Surgery | Post-operative swelling, Lymph fluid buildup |
**Surgical interventions** for cancer, especially those involving lymph node removal, can disrupt the body’s natural drainage system. This can result in lymphedema, a specific type of edema characterized by longer-term fluid buildup. Post-surgical care often includes:
- **Physical therapy** to promote fluid movement
- **Compression bandages** to support the area
- **Elevating affected limbs** when possible
Addressing these issues early is crucial to preventing severe complications and enabling smoother recovery.

Proactive Strategies to Minimize Edema During Chemotherapy
One effective approach to minimizing edema during chemotherapy is maintaining **adequate hydration**. While it may seem counterintuitive, drinking plenty of fluids can help flush excess salt out of the body, which in turn reduces water retention. This can be achieved by:
- Drinking water throughout the day, aiming for at least 8 cups daily.
- Incorporating hydrating foods like cucumbers, tomatoes, and watermelons into meals.
- Avoiding beverages that contribute to dehydration, such as alcohol and caffeine.
Proper dietary choices play a crucial role in managing edema as well. A diet low in sodium can prevent the body from retaining excessive fluids. Here are some tips for a low-sodium diet:
- Choosing fresh, unprocessed foods over canned or packaged items.
- Using herbs and spices to season food instead of salt.
- Reading food labels carefully to check for sodium content.
Gentle exercise can also aid in reducing swelling. Physical activity encourages blood circulation and helps remove fluid from swollen areas. Suitable exercises might include:
- Walking or slow-paced jogging for 20-30 minutes daily.
- Engaging in light yoga or stretching routines.
- Practicing water-based exercises, such as swimming or aquatic aerobics.
Lastly, consider the importance of **elevating the legs** to reduce lower limb edema. Elevation facilitates the return of fluid to the circulatory system and alleviates pressure in the swollen areas. Follow these positioning tips:
| Elevation Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Leg Positioning | Prop legs above heart level using pillows. |
| Rest Intervals | Take breaks throughout the day to elevate legs for 15-20 minutes. |
| Sleeping Position | Elevate feet slightly while sleeping. |
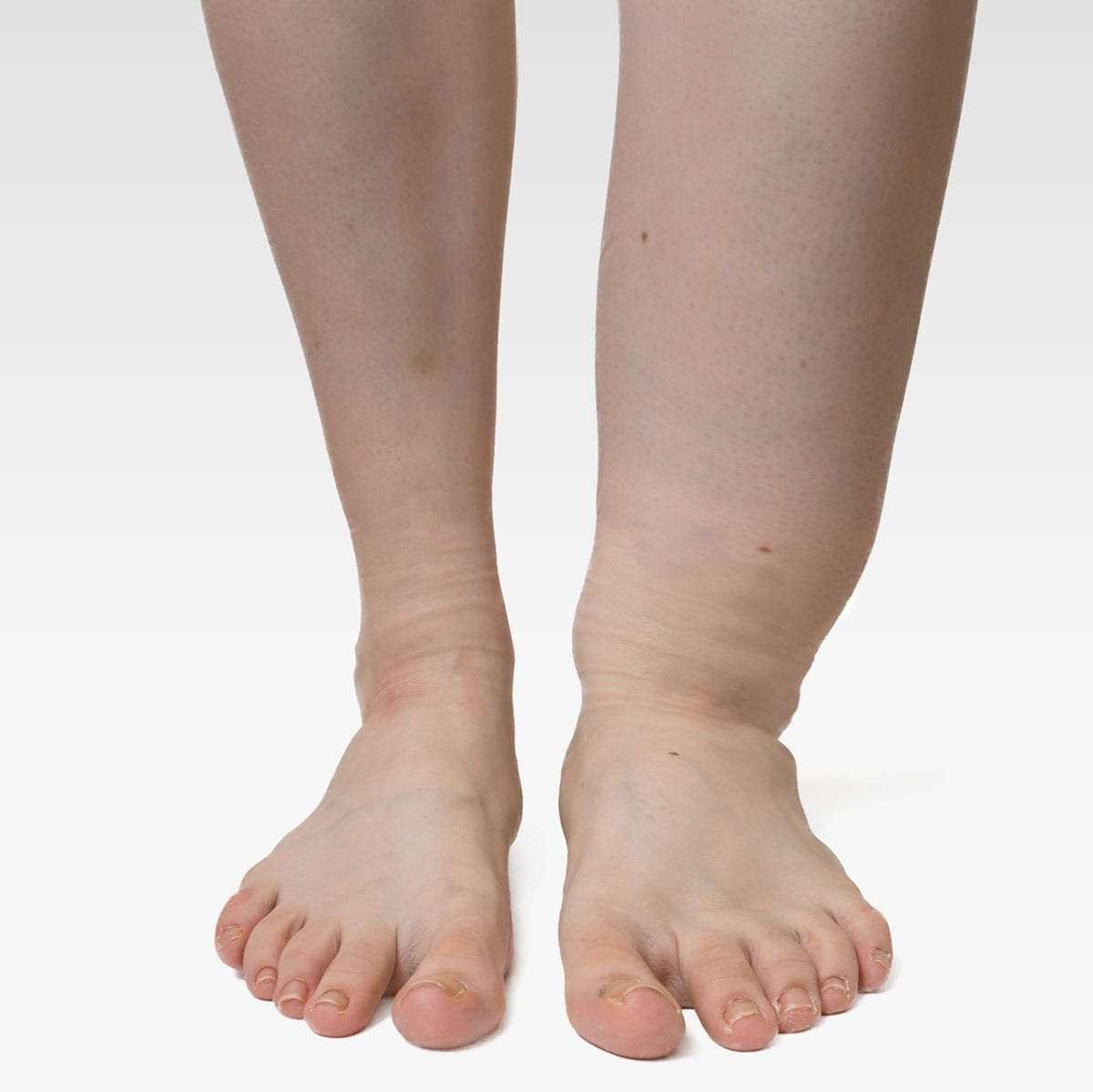
Daily Habits and Lifestyle Changes to Manage Edema Effectively
Coping with edema during cancer treatment requires adopting daily habits and lifestyle changes that can make a significant difference. First and foremost, maintaining a balanced diet that is low in sodium is crucial. Excess salt can lead to fluid retention, exacerbating edema. Incorporate **nutrient-rich foods** like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall health. Staying hydrated is equally important, as it helps flush out excess sodium and toxins from your body.
- **Limit your intake of processed and salty foods.**
- **Focus on a diet rich in potassium,** such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach, which help balance sodium levels.
- **Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day** to stay adequately hydrated.
Physical activity can also play a pivotal role in managing edema. Regular exercise, such as **walking or gentle yoga**, can help improve circulation and reduce swelling. If you’re experiencing severe edema, consider exercises that don’t put excessive strain on your affected limbs. Elevating the legs above heart level for at least 30 minutes daily can also help reduce fluid build-up. Consult your healthcare provider for guidance on tailored exercises suitable for your condition.
| Weekly Exercise Routine | Duration |
|---|---|
| Walking | 30 minutes, 5 days a week |
| Gentle Yoga | 20 minutes, 3 days a week |
| Leg Elevation | 30 minutes daily |
Another critical aspect is wearing proper compression garments. These specially designed socks or sleeves can help prevent fluid from accumulating in your limbs. Make sure they fit well and provide the right amount of pressure. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate some of the pressure on your blood vessels and reduce the symptoms of edema. Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider are vital to monitor your condition and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.

Advanced Medical Interventions and Supportive Therapies for Edema
Effectively managing edema in cancer patients often necessitates the use of advanced medical interventions. **Diuretics**, commonly known as water pills, are frequently prescribed to help reduce fluid accumulation. They work by increasing the kidneys’ production of urine, thereby reducing the volume of fluid in the body. Diuretics are generally categorized into three main types: thiazide, loop, and potassium-sparing. Each type has a specific mechanism of action and set of applications, making it crucial for healthcare providers to tailor the treatment to the individual needs of the patient.
Compression therapy is another key intervention employed to address edema. This therapeutic modality involves the use of specially designed garments such as stockings, sleeves, or gloves to exert controlled pressure on the affected areas. The underlying principle is to promote the movement of fluid through the lymphatic system, thereby reducing swelling. For individuals battling cancer, custom-fitted compression garments can be particularly beneficial as they provide support without interfering with ongoing treatments or contributing to discomfort.
In addition to medical interventions, a range of supportive therapies can significantly aid in managing edema. **Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)** is a specialized form of massage that encourages lymph fluid circulation and helps reduce swelling. Differing from traditional massage techniques, MLD utilizes light, rhythmic strokes to stimulate lymphatic flow and enhance the body’s natural drainage process. Patients often find MLD sessions to be not only effective but also relaxing, making it a dual-purpose treatment offering both physical relief and emotional comfort.
| Intervention | Description |
|---|---|
| Diuretics | Medications that increase urine production to reduce fluid accumulation. |
| Compression Therapy | Use of garments to exert pressure and promote fluid movement. |
| Manual Lymphatic Drainage | A specialized massage technique to stimulate lymphatic flow. |
Electrolyte management is another supportive measure that warrants attention. Sudden changes in the body’s fluid levels can disrupt the balance of electrolytes, leading to complications such as muscle cramps, weakness, and cardiac issues. Healthcare providers may recommend specific dietary adjustments or supplements to help stabilize electrolyte levels. For instance, increasing the intake of foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and calcium can often counteract imbalances caused by fluid shifts. Careful monitoring and tailored nutritional strategies are essential to ensure that these supportive therapies are both safe and effective for each unique patient case.
Q&A
Q: What is edema, and how is it related to cancer treatment?
A: Edema is the medical term for swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body’s tissues. It often manifests in the extremities, such as the legs, feet, and hands, but can occur anywhere in the body. In the context of cancer treatment, edema can arise as a side effect of certain therapies, such as chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery, which may interfere with the normal functioning of the lymphatic or cardiovascular systems.
Q: Why is it important to manage edema during cancer treatment?
A: Managing edema is crucial during cancer treatment because excessive swelling can lead to significant discomfort, reduced mobility, and a higher risk of infections. Effective management ensures that patients maintain their quality of life and continue their treatment regimen without unnecessary complications.
Q: What strategies can help in managing edema for cancer patients?
A: Several strategies can be employed to manage edema in cancer patients, including:
- Medication: Diuretics may be prescribed to help the body expel excess fluids through urine.
- Compression garments: Wearing compression stockings or sleeves can help prevent fluid accumulation in the extremities.
- Elevation: Regularly elevating the affected limbs above heart level can encourage fluid drainage.
- Diet: Reducing sodium intake can help minimize fluid retention.
- Physical activity: Gentle exercises like walking or swimming can stimulate circulation and lymphatic drainage.
- Manual lymphatic drainage: A specialized massage technique can aid in the movement of lymphatic fluid.
Q: Are there specific lifestyle changes that can help manage edema?
A: Yes, adopting certain lifestyle changes can make a significant difference. These include:
- Staying hydrated but avoiding excessive fluid intake.
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while minimizing salt and processed foods.
- Wearing loose, comfortable clothing to avoid constriction around swollen areas.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the lymphatic and cardiovascular systems.
Q: How can healthcare providers support patients dealing with edema during cancer treatment?
A: Healthcare providers can play a pivotal role by:
- Monitoring the patient’s condition regularly and adjusting treatment protocols as necessary.
- Educating patients about the signs and symptoms of edema and effective management techniques.
- Providing referrals to specialists, such as physiotherapists or nutritionists, who can offer additional support and tailored strategies.
- Encouraging open communication so patients feel comfortable discussing their symptoms and any difficulties they encounter.
Q: What should patients do if they experience severe or worsening edema?
A: If edema becomes severe or rapidly worsens, patients should contact their healthcare provider immediately. Severe edema can signal potentially serious complications that require prompt medical attention, such as deep vein thrombosis or heart issues. Early intervention can prevent further complications and help manage symptoms effectively.
By understanding the nature of edema and employing a combination of medical and lifestyle strategies, cancer patients can navigate their treatment journey with greater confidence and comfort.
Concluding Remarks
As we navigate the intricate maze of cancer treatment, managing edema emerges not just as a necessary medical endeavor but as an art of balancing compassion with precision. This journey demands vigilance, resilience, and most importantly, a holistic approach that encompasses the patient’s physical, emotional and psychological well-being. By unraveling the intricate threads that weave through treatment regimens and supportive care, we can empower those affected to not just endure, but to thrive amidst their challenges.
In the realm of cancer care, every step toward understanding and mitigating edema represents a step toward a more hopeful horizon. With every pulse beat of scientific advancement and every compassionate gesture from a caregiver, we inch closer to a world where the burdens of treatment are softened, and the path forward is illuminated with care and grace.
As we close this chapter on managing edema in cancer treatment, let us carry forward the knowledge and empathy gained. For in the stories of those who face the storm with unwavering spirit, we find a profound reminder of the human capacity to persevere, adapt, and find grace even in the most daunting of trials. Here’s to a future where cancer care continues to evolve, enveloped in a cocoon of understanding and unwavering support.